Volcano Watch: Kīlauea’s south flank hasnʻt had a slow slip event in 7 years and is overdue
“Volcano Watch” is a weekly article and activity update written by scientists and affiliates with the U.S. Geological Survey Hawaiian Volcano Observatory. Today’s article is by research geophysicist Ingrid Johanson.
Over the past two decades, scientists and members of the public have anticipated the occurrence of slow slip events on Kīlauea’s south flank. These events are recorded by the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory’s continuous GPS network, which show as much as 0.75 inches of increased seaward motion of the flank over 2 to 3 days — equivalent to about a magnitude 6 earthquake.
South flank slow slip events occur on the nearly-flat decollement fault that sits 4 to 5 miles below the ground surface at the interface of Kīlauea and the preexisting ocean floor. The decollement fault can slip in large earthquakes, as well as via steady creep. “Steady creep” means that portions of the decollement fault are continuously sliding very slowly.
Because of their slow speed, slow slip events do not generate the seismic waves that cause hazardous shaking. Thus, both steady creep and slow slip events safely release stress.
After 2005, slow slip events on Kīlauea’s south flank occurred every 2.5 years, give or take 3 months. These included events in June 2007, February 2010, May 2012 and October 2015. The Hawaiian Volcano Observatory anticipated that another slow slip event would happen between February and August of 2018.
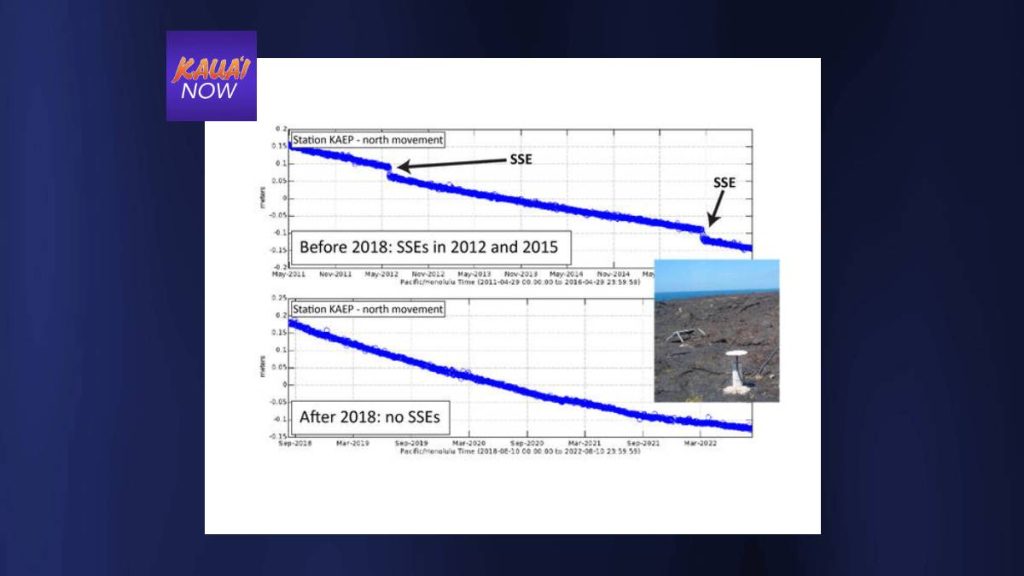
Instead, the lower East Rift Zone eruption of Kīlauea began May 3, 2018. If a slow slip event had occurred during this eruption, the unique spatial and temporal pattern in the continuous GPS would have still been detectable. However, no slow slip event occurred.
Furthermore, there has not been another slow slip event on Kīlauea’s decollement fault since 2018. It has now been just over seven years since the last one occurred in 2015. One reason for this may be the magnitude 6.9 earthquake that occurred on May 4, 2018, just after the first lower East Rift Zone eruptive vent opening.
The variety of slip behaviors (earthquakes, creep, slow slip events) on the decollement fault suggests that the fault has zones with different frictional properties. Some areas have “velocity-weakening” frictional properties, which allows them to initiate (nucleate) earthquakes, and some areas have “velocity-strengthening” friction, which leads to steady creep. Slow slip events can occur in “velocity-strengthening” regions, but can also be an indication that the frictional properties of the fault are more complicated.
“Velocity-weakening” frictional properties are something most of us a familiar with. If you’re trying to move a heavy box, you just need to get the box sliding a little bit before it moves easily. This is because the strength of the frictional force between the box and floor goes down once it starts sliding.
Earthquakes occur as quickly as they do because once the stress on the fault is high enough to slide it a little (nucleate), it becomes easier to continue slipping until the excess stress is used.
“Velocity-strengthening” friction is less intuitive; its more similar to “drag” processes. If you have ever tried to quickly wade through knee-deep water, then you may remember that it gets harder, the faster you try to move. The best strategy is to choose a slow even pace, one that matches the drag force of the water to your strength.
In the same way, faults with velocity-strengthening friction must release their stress slowly and evenly, balancing the frictional force that increases as they slide, to the driving stress.
So why would the magnitude 6.9 earthquake prevent slow slip events from occurring? Although earthquakes can’t nucleate in velocity-strengthening regions, if an earthquake starts with enough energy, it can grow into a slow slip event region.
The effect is somewhat like running from shore into the ocean; you might get far if you start with enough speed. This is what the 2018 magnitude 6.9 earthquake did; its epicenter was offshore and west of Kalapana, but the earthquake involved slip on a 16-mile length of the fault, stretching to the west and including the region of the decollement fault that produced slow slip events.
The massive stress release of the earthquake rupture means that the section of the fault that produced slow slip events may need time before it has built enough stress to start producing slow slip events again.
Observing what happens next and what (if anything) brings the slow slip events back could provide a fascinating view into the frictional properties of Kīlauea’s south flank decollement fault. The massive changes that the 2018 eruption brought to the landscape and to Kīlauea will continue to drive interesting science for years to come.



